Our recent paper Deciphers TAL effectors for 5-methylcytosine and 5-hydroxymethylcytosine recognition
Our new article named “Deciphering TAL effectors for 5-methylcytosine and 5-hydroxymethylcytosine recognition” has been published in Nature Communications (https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-017-00860-6).
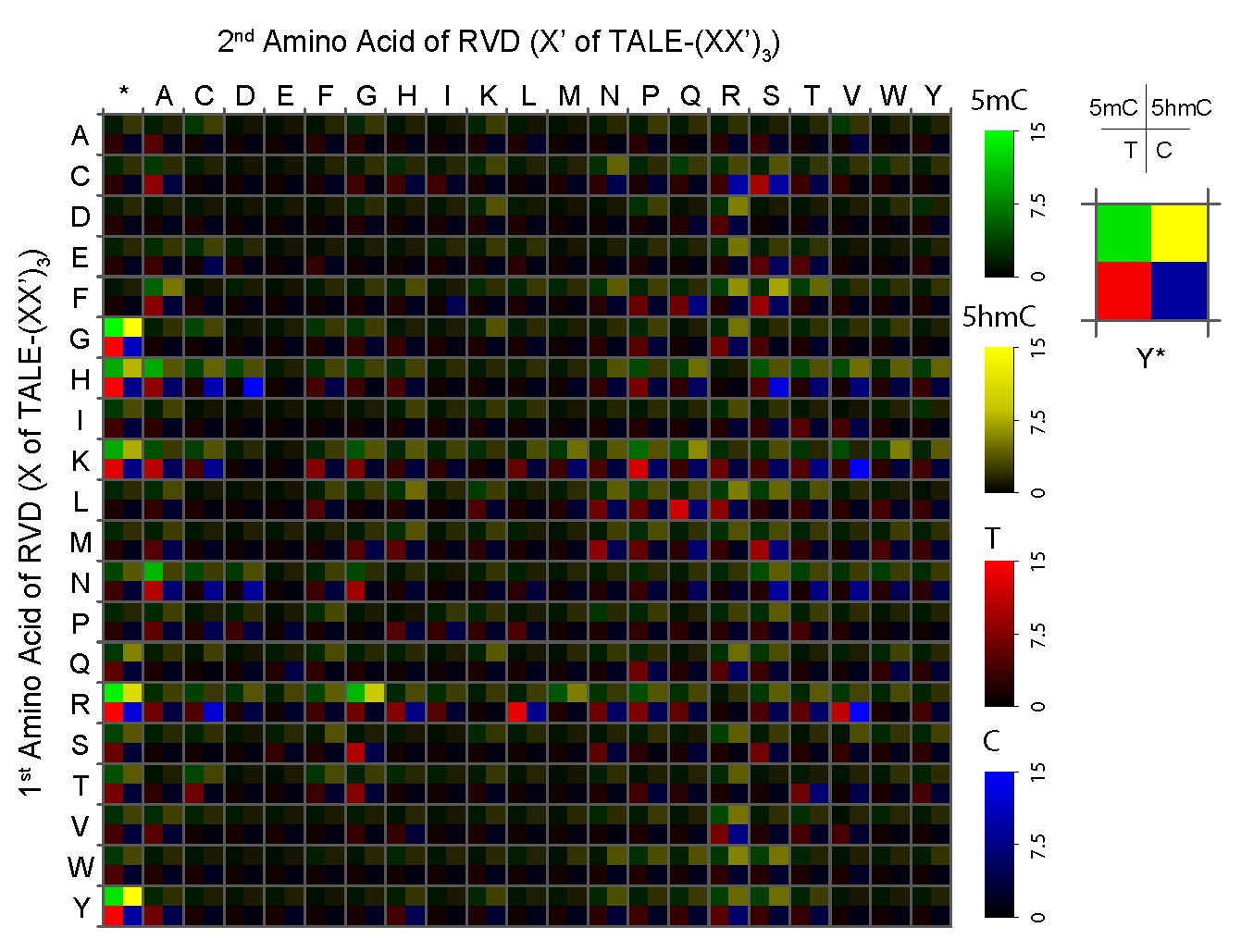
DNA recognition by transcription activator-like effector (TALE) proteins is mediated by tandem repeats that specify nucleotides through repeat-variable diresidues (RVDs). RVDs form direct and sequence-specific contacts to DNA bases; hence, TALE-DNA interaction is sensitive to DNA chemical modifications. Here, we conduct a thorough investigation, covering all theoretical RVD combinations, for their recognition capabilities for 5-methylcytosine (5mC) and 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5hmC), two important epigenetic markers in higher eukaryotes. We identify both specific and degenerate RVDs for 5mC and 5hmC. Utilizing these novel RVDs, we achieve methylation-dependent gene activation and genome editing in vivo; we also report base-resolution detection of 5hmC in an in vitro assay. Our work deciphers RVDs for 5mC and 5hmC, and provides tools for TALE-dependent epigenome recognition.